Mangiferin: A Powerful Bioactive Compound with Untapped Potential Therapeutic Properties
Mangiferin is a highly beneficial bioactive compound found in various parts of the mango tree, including the fruit, bark, and leaves. It belongs to the class of compounds called xanthones, known for their potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. One of the most significant benefits of mangiferin is its anti-inflammatory
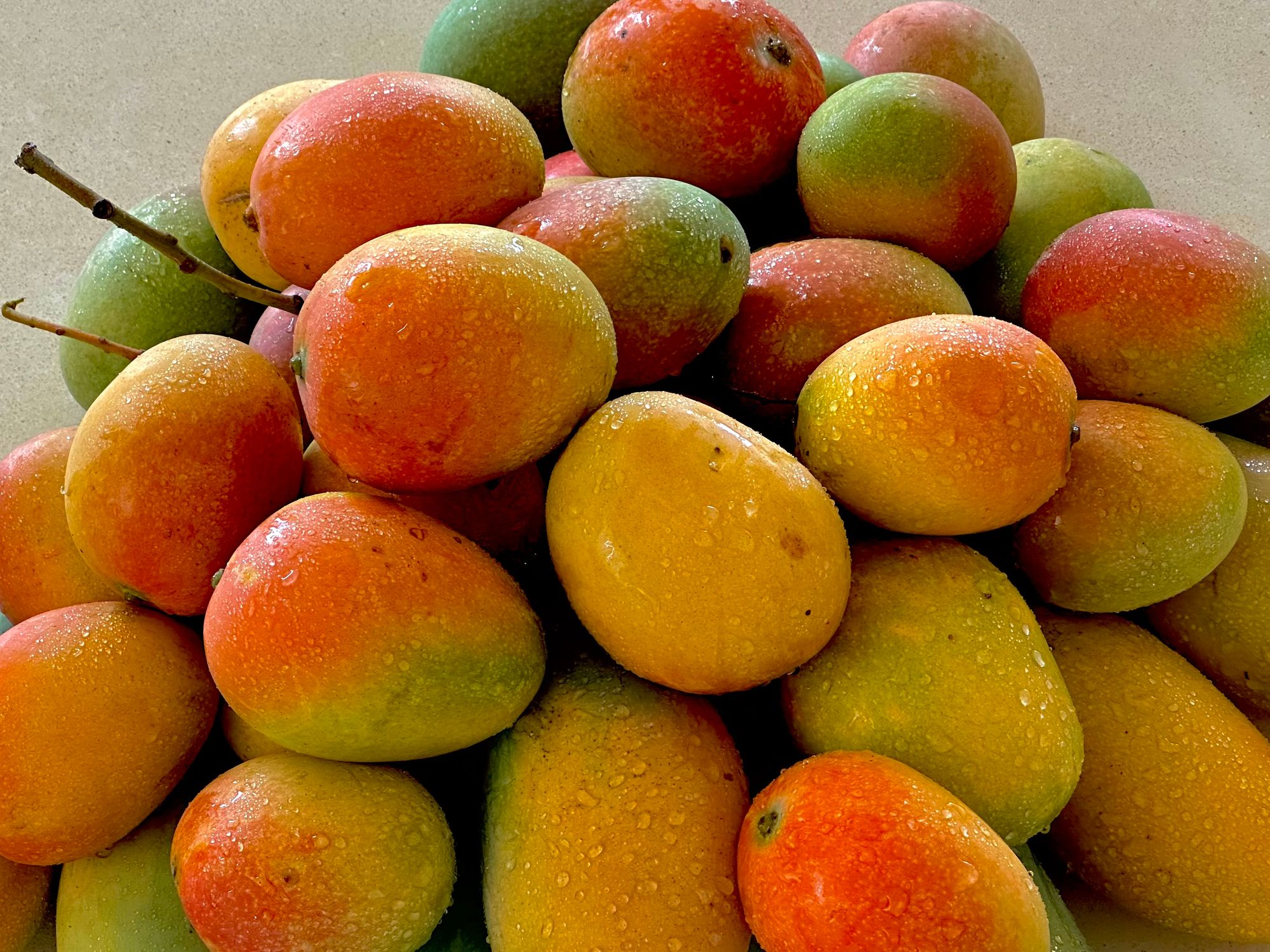

Mangiferin is a highly beneficial bioactive compound found in various parts of the mango tree, including the fruit, bark, and leaves. It belongs to the class of compounds called xanthones, known for their potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties.
One of the most significant benefits of mangiferin is its anti-inflammatory properties, which may help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as arthritis and heart disease. Additionally, the compound has potent antioxidant effects that help protect our cells from oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
Studies have also suggested that mangiferin may have anticancer properties by inhibiting cancer cell growth and inducing programmed cell death, or apoptosis, in cancer cells.
Furthermore, mangiferin has potential antidiabetic effects as it helps regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Additionally, the compound may have neuroprotective effects that protect the brain from inflammation and oxidative stress-induced damage.
Mangiferin is a promising bioactive compound with numerous potential health benefits. Although further research is required to fully understand the compound's mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications, it is clear that mangiferin plays a critical role in the nutritional and medicinal properties of mangoes, particularly those grown in Mexico.
In Mexico, mangoes are a vital part of the culture, cuisine, and economy. The country is one of the largest producers of mangoes globally, with many small farmers relying on mango cultivation for their livelihoods. The fruit is enjoyed in various forms, including fresh, dried, pickled, and in various dishes such as salsas, smoothies, and desserts.
The mango tree is also a symbol of cultural identity and heritage, with its imagery featuring in art, music, and literature. Additionally, the tree is considered sacred in some Mexican indigenous communities, and its bark and leaves are used in traditional medicine.